
Digital Terrain Data create contour mapĤ.) Here you can determine the coordinates of the tile in which your location is lying. You can read the documentation for information. Click on SRTM 3.ģ.) Click on large map.
DIGITAL TERRAIN MODEL,DTM DOWNLOAD
Download Digital Terrain Data:Ģ.) Digital Terrain data is all we need.
DIGITAL TERRAIN MODEL,DTM HOW TO
Here you will find how to download Digital Terrain Data and create contour map. We don’t have to do hectic work like this as webgis provides us with ready-made digital elevation data. WebGIS is where you can find all the leading information and resources for Geographical Information Systems. It is generated by collecting elevation points of terrain. A DTM represents distinctive terrain features much better because of its 3D breaklines and regularly spaced 3D mass points.Digital Elevation Model is a 3D representation of a terrain. From these regularly-spaced contour lines, you can interpolate a DTM into a DEM. In the image above, you can see how the DTM is not continuous and that it’s not a surface model. The DTM points are regularly-spaced and characterize the shape of the bare-earth terrain. For example, contour lines are in purple. A DTM augments a DEM by including linear features of the bare-earth terrain.ĭTMs are typically created through photogrammetry as in the example above. A DTM is a vector data set composed of regularly spaced points and natural features such as ridges and breaklines.
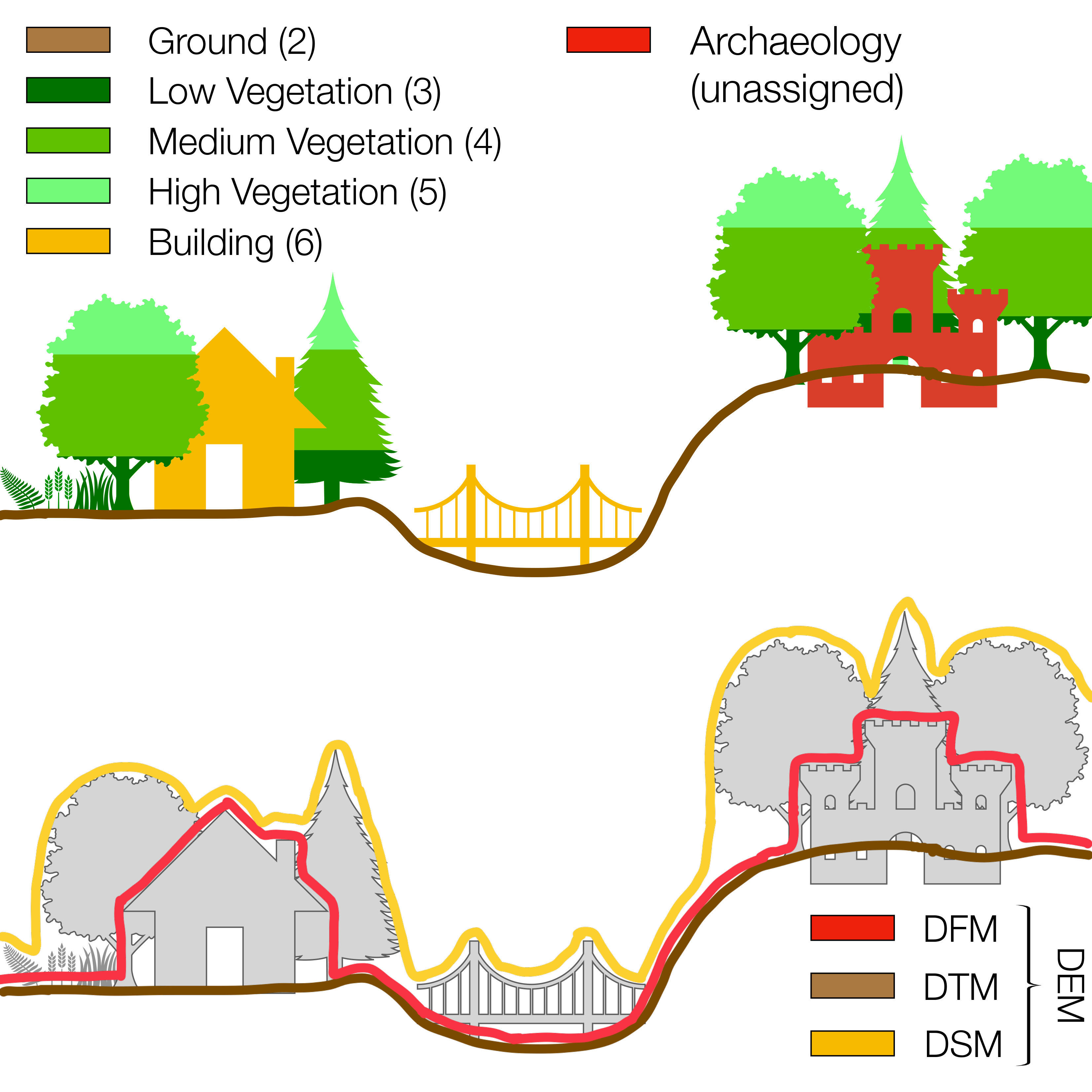
This means that a DTM is simply an elevation surface representing the bare earth referenced to a common vertical datum.
DIGITAL TERRAIN MODEL,DTM FREE
READ MORE: Free Global DEM Data Sources – Digital Elevation Models SOIL MAPPING: DEMs assist in mapping soils which is a function of elevation (as well as geology, time, and climate). This is useful when planning a highway or residential subdivision. TERRAIN STABILITY: Areas prone to avalanches are high slope areas with sparse vegetation. HYDROLOGIC MODELLING: Hydrologists use DEMs to delineate watersheds, calculate flow accumulation and flow direction. A bare-earth elevation model is particularly useful in hydrology, soils, and land use planning When you void vegetation and man-made features from elevation data, you generate a DEM. The built (power lines, buildings, and towers) and natural (trees and other types of vegetation) aren’t included in a DEM. When you filter out non-ground points such as bridges and roads, you get a smooth digital elevation model.
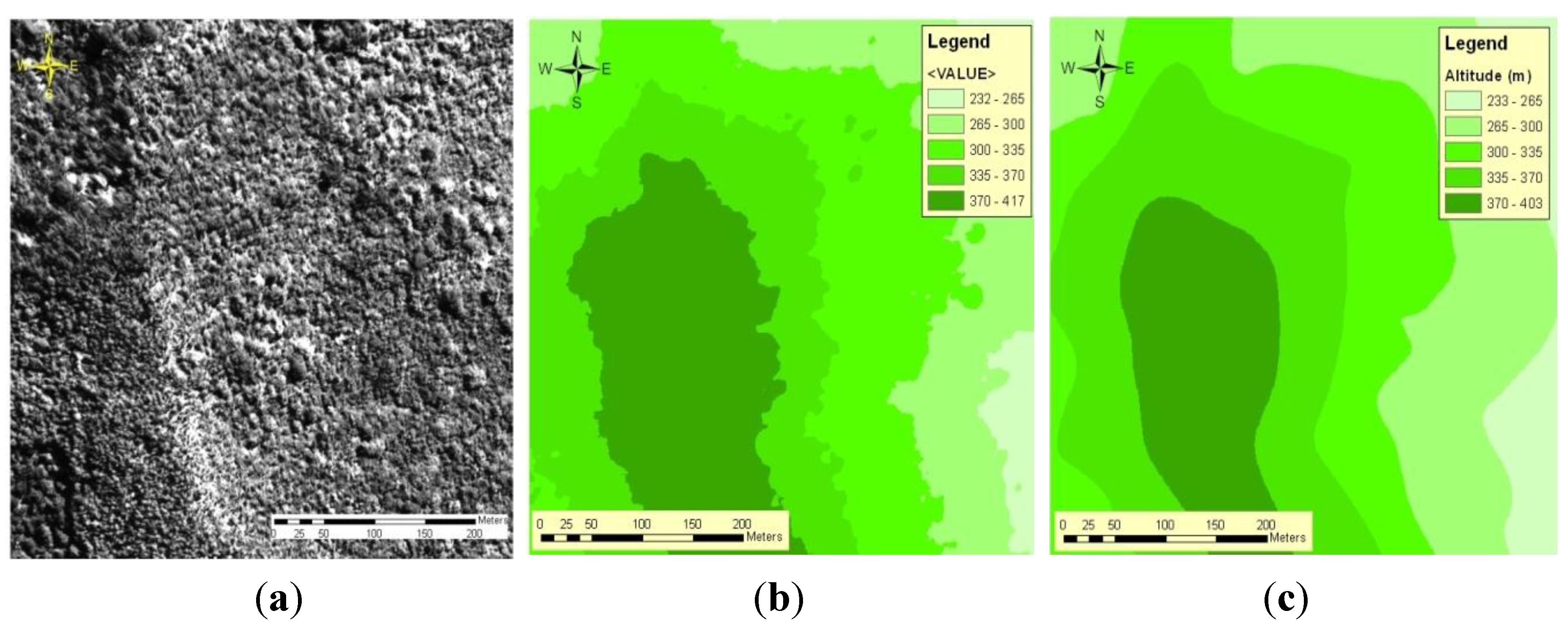

VIEW OBSTRUCTION: Urban planners use DSM to check how a proposed building would affect the viewshed of residents and businesses.Ī digital elevation model is a bare-earth raster grid referenced to a vertical datum. VEGETATION MANAGEMENT: Along a transmission line, DSMs can see where and how much vegetation is encroaching. RUNWAY APPROACH ZONE ENCROACHMENT: In aviation, DSMs can determine runway obstructions in the approach zone. Because objects extrude from the Earth, this is particularly useful in these examples: Digital Surface Model (DSM) – Extruding features are tree canopy A DSM captures the natural and built features on the Earth’s surface.Ī DSM is useful in 3D modeling for telecommunications, urban planning and aviation. But height can come from the top of buildings, tree canopy, powerlines, and other features.

In the end, LiDAR delivers a massive point cloud with elevation values. Hence, how this system earned its name of Light Detection and Ranging. When the pulse of light bounces off its target and returns to the sensor, it gives the range (a variable distance) to the Earth. In a LiDAR system, pulses of light travel to the ground. What is a Digital Surface Model (DSM)? Airborne Light Detection and Ranging (LiDAR)


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
